The Age of Imperialism from the late 19th century
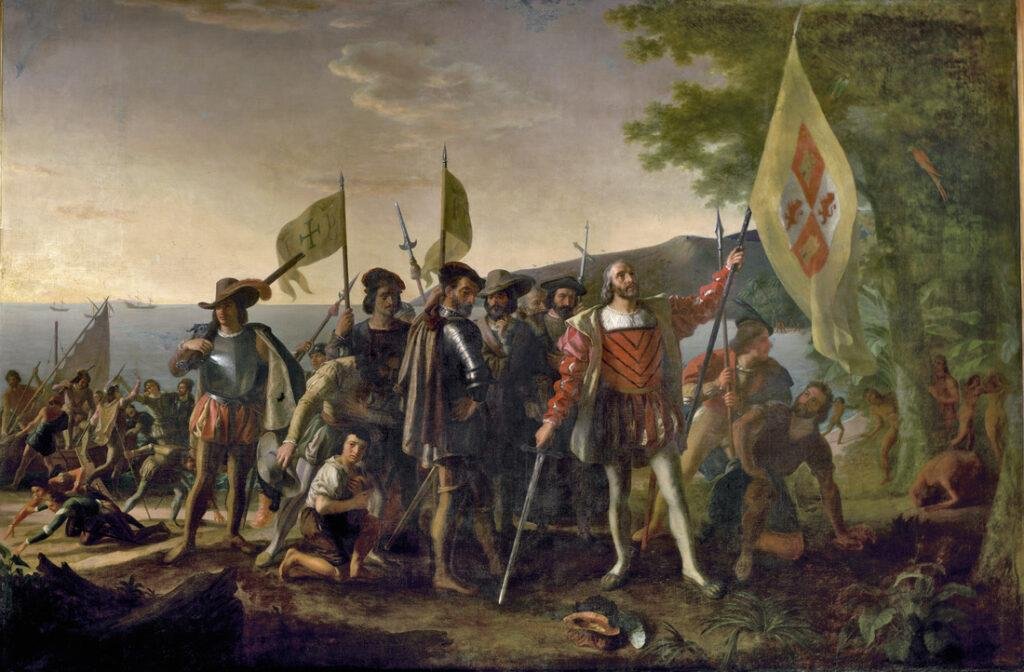
The Age of Imperialism, which lasted from the late 19th century to the early 20th century, was a period of intense competition among European powers for control of territories outside of Europe.
During this time, European powers established colonies and controlled territories in Asia, Africa, and the Americas. The effects of imperialism on the colonized peoples and nations were significant and far-reaching, shaping the political, social, and economic structures of these societies for decades to come.
One of the most significant effects of imperialism on the colonized peoples and nations was the loss of political autonomy and self-determination. European powers imposed their own political systems and structures on the colonies, often with little regard for the cultural or historical context of these societies.

This resulted in the suppression of local political and social institutions and the imposition of European-style bureaucracy and administration.
Loss of autonomy led to economic implications, with European powers extracting resources and labor from colonies. Europe’s industrial economy was fueled by exploiting colonies for resources like rubber, minerals, and oil.
The exploitation of labor was also widespread, with many colonies forced to supply cheap labor to European businesses and industries.
Imperialism also had a significant impact on the social structures of the colonized societies. European powers imposed their cultural norms on colonies, suppressing local languages, customs, and religions.
This resulted in the loss of cultural identity and the erosion of traditional social structures.
Imperialism also had a profound impact on the colonized peoples’ sense of identity and self-worth. Colonial societies faced European racism, reinforcing the notion of European superiority over non-European peoples.
This created a legacy of social and psychological damage that persists to this day.
The effects of imperialism on the colonized nations were also significant. Colonies often inherited unsuitable political and economic systems that perpetuated exploitation and oppression.
Imperialism’s legacies persist in post-colonial nations’ economic and political structures, leading to corruption, poverty, and instability.
In addition, imperialism had a significant impact on global politics and power dynamics. Colonizing territories outside Europe granted economic and military advantages, bolstering European dominance in global affairs.
This marginalized non-European nations, denying access to resources needed for global competition.
The effects of imperialism on the colonized peoples and nations were complex and varied. Imperialism introduced benefits like technology and infrastructure, but the negative consequences of European domination overshadowed them.
Imperialism’s legacy persists globally, with nations and people grappling to overcome its political, economic, and social effects.
Conclusion
The Age of Imperialism was a period of intense competition among European powers for control of territories outside of Europe.
Imperialism significantly shaped colonized societies’ political, social, and economic structures for decades.
While imperialism brought benefits, the ongoing negative consequences of European domination often overshadowed them. 온라인카지노