Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was a profound and transformative period that began in the late 18th century and extended well into the 19th century.
The Industrial Revolution originated in Britain, fueled by a combination of factors, including advancements in agriculture, a growing population, access to natural resources, and a progressive mindset that embraced innovation.
It marked a revolutionary shift in economic, social, and technological spheres, fundamentally changing the way societies functioned and paving the way for modern industrialized nations.
One of the primary catalysts was the development of new machinery and manufacturing processes, driven by the mechanization of textile production. The invention of the spinning jenny, water frame, and steam engine revolutionized production, significantly increasing output while reducing costs.
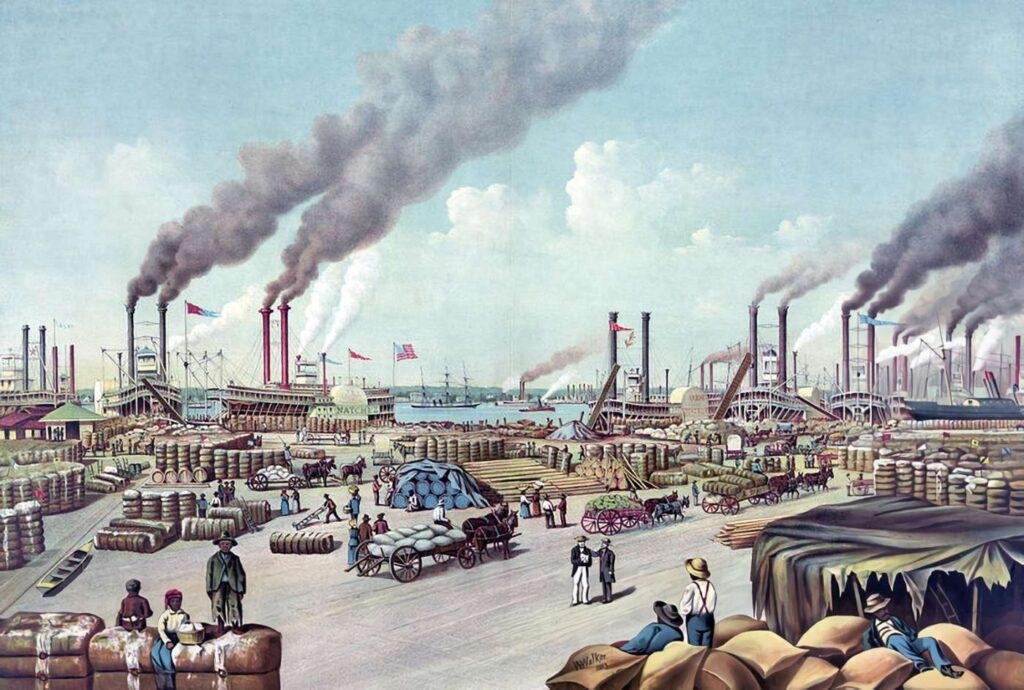
This transformation in production methods extended to other industries as well, including iron and coal mining, transportation, and agriculture.
Steam engines, powered by coal, played a pivotal role in revolutionizing transportation with railways and steamships.
The Industrial Revolution brought about significant changes in society. It led to rural-urban migration, as people moved from the countryside to cities in search of employment opportunities in factories.
This shift from agrarian-based economies to industrialized urban centers fundamentally altered the demographic landscape.
Urbanization and industrial concentration in cities led to a working-class population enduring long hours and harsh conditions. Labor unions emerged, advocating for workers’ rights and eventually leading to improved working conditions and labor laws.
The Industrial Revolution also brought about changes in social classes and economic structures.
It led to a wealthy capitalist class investing in industries, while many faced economic hardships and increased social stratification.
In addition to the social and economic impacts, the Industrial Revolution had profound effects on culture, education, and technology. It spurred advancements in science and technology, paving the way for subsequent waves of innovation.
While the Industrial Revolution brought about immense progress and improved living standards for many, it also had negative consequences. Exploitative labor practices, environmental degradation, and overcrowded urban conditions were among the challenges that emerged during this period.
The Industrial Revolution’s effects spread worldwide, forming a global industrialized economy in Europe, North America, and beyond.
Conclusion
The Industrial Revolution stands as a defining period in human history, fundamentally reshaping societies and economies worldwide.
It triggered tech progress and economic growth while emphasizing the importance of addressing social inequalities and environmental sustainability.
Today, it serves as a reminder of human ingenuity and the importance of balanced progress benefiting all of society. 바카라사이트

